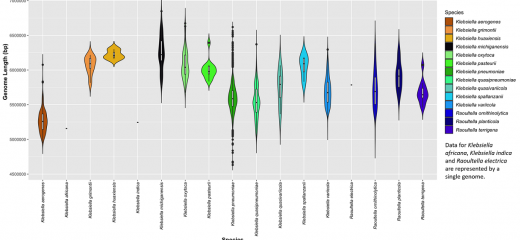
Explore the genome size of the 17 Klebsiella and related Raoultella species
Klebsiella species are highly diverse including the size of the genome and genetic information they carry. Klebsiella species are able to acquire additional DNA in the form of extrachromosomal elements, such as plasmids and exchange these with other bacterial species. This is a common way they acquire and share antibiotic resistance and virulence genes amongst bacterial communities. Klebsiella species can acquire multiple plasmids, which can very in size.
Investigate the data using different type of visualisation which can be selected by clicking on the boxes below, e.g. Box Plot, Scatter Plot etc. Hovering over the display will display the minimum, median and maximum species size.
Klebsiella/Raoultella Species
| Species | Isolates (n) | Species | Isolates (n) | Species | Isolates (n) | Species | Isolates (n) | Species | Isolates (n) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K. africana | 1 | K. indica | 1 | R. electrica | 1 | K. huaxiensis | 3 | K. spallazanii | 4 | ||
| K. quasivaricola | 6 | K. grimontii | 8 | R. terrigena | 10 | K. pasteurii | 13 | R. planticola | 29 | ||
| R. ornithinolytica | 62 | K. michiganensis | 73 | K. oxytoca | 110 | K. aerogenes | 238 | K. variicola | 287 | ||
| K.quasipneumoniae | 299 | K. pneumoniae | 9048 | ||||||||
| https://pubmlst.org/rmlst | |||||||||||